Nowadays, the automotive industry is witnessing a significant shift towards greener and more sustainable technologies. As the world strives to reduce its carbon footprint and combat climate change, alternative fuel sources are becoming increasingly important. Two promising contenders in the realm of sustainable transportation are hydrogen and electric engines. In this article, we will delve into the characteristics, advantages, limitations, and future prospects of both hydrogen and electric engine cars. So, let’s dive in and explore the exciting world of automotive innovation.
Introduction
In recent years, hydrogen engine cars have gained attention as a potential game-changer in the automotive industry. These vehicles utilize hydrogen gas as a fuel source, which is converted into electricity through a chemical reaction in the engine. On the other hand, electric engine cars rely on electricity stored in batteries for their operation. Both technologies offer unique benefits and face their own set of challenges, prompting a debate over which one will dominate the future of transportation.![]()
What is a Hydrogen Engine?
A hydrogen engine, also known as a hydrogen fuel cell engine, is a type of internal combustion engine that uses hydrogen gas as its primary fuel. Hydrogen, a versatile and abundant element, is combined with oxygen from the air to produce electricity, with water vapor being the only by-product. This makes hydrogen engines emission-free, as they release no harmful pollutants or greenhouse gases.

How Hydrogen Engines Work
Hydrogen engines operate through a process called electrolysis, where hydrogen is extracted from a storage tank and combined with oxygen from the air in a fuel cell stack. This chemical reaction generates electricity, which is then used to power the vehicle’s electric motor. The only by-product of this reaction is water vapor, making hydrogen engines a clean and sustainable solution for transportation.![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Advantages of Hydrogen Engine Cars
Zero Emissions: Hydrogen engines produce no harmful emissions, contributing to cleaner air and reduced greenhouse gas emissions.
Fast Refueling: Hydrogen cars can be refueled in a matter of minutes, similar to traditional gasoline-powered vehicles.
Long Driving Range: Hydrogen engine cars offer a longer driving range compared to many electric vehicles, making them suitable for long-distance travel.
Limitations of Hydrogen Engine Cars
Limited Infrastructure: Hydrogen refueling stations are still relatively scarce, limiting the widespread adoption of hydrogen engine cars.
Cost: Currently, hydrogen engine cars tend to be more expensive than their electric counterparts, primarily due to the high cost of hydrogen production and storage technologies.
Energy Efficiency: Hydrogen production and distribution processes can result in energy losses, making the overall energy efficiency of hydrogen engine cars lower than electric vehicles.
What is an Electric Engine?
An electric engine, also known as an electric motor, is a device that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy to propel a vehicle. Electric vehicles (EVs) rely on rechargeable batteries to store electrical energy, which is then used to power the motor.![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
How Electric Engines Work
Electric engines work based on the principle of electromagnetism. When an electric current passes through a wire coil placed within a magnetic field, it generates rotational motion, which is harnessed to drive the vehicle’s wheels. The electrical energy required to power the motor is stored in high-capacity batteries that can be charged using a charging station or a standard electrical outlet.
Advantages of Electric Engine Cars
Zero Emissions: Electric vehicles produce no tailpipe emissions, contributing to cleaner air and reduced carbon footprint.
Energy Efficiency: Electric engines offer higher energy efficiency compared to internal combustion engines, resulting in lower energy consumption per mile.
Lower Operating Costs: Electric vehicles generally have lower operating costs than traditional gasoline-powered cars, as electricity is often cheaper than gasoline.
Limitations of Electric Engine Cars
Limited Range: Electric vehicles typically have a limited driving range compared to hydrogen engine cars, although this is improving with advancements in battery technology.
Charging Infrastructure: The availability of charging infrastructure, including public charging stations, is still a challenge in some regions, causing range anxiety among potential EV buyers.
Charging Time: Charging an electric vehicle can take significantly longer than refueling a hydrogen engine car, although fast-charging technology is being developed to minimize charging times.
Hydrogen vs. Electric: A Comparison
When comparing hydrogen and electric engine cars, several factors come into play, including environmental impact, infrastructure challenges, and cost considerations. Each technology has its own strengths and weaknesses, and their suitability depends on specific use cases and regional factors.
Environmental Impact of Hydrogen and Electric Cars
Both electric cars and hydrogens cars have a significantly lower environmental impact compared to conventional vehicles. However, the sources of electricity generation play a crucial role in determining the overall carbon footprint. If the electricity used to produce hydrogen is derived from renewable sources, hydrogen cars can be considered truly sustainable. Likewise, if the electricity used to charge electric vehicles comes from renewable sources, their environmental benefits are maximized.![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Infrastructure Challenges
One of the key challenges for widespread adoption of hydrogen engine cars is the limited infrastructure for hydrogen refueling stations. Establishing a comprehensive network of refueling stations requires significant investments and coordination among various stakeholders. On the other hand, the electric vehicle charging infrastructure is more prevalent, although further expansion is needed to address range anxiety and cater to the growing number of EVs on the road.
Cost Considerations
Currently, hydrogen engine cars tend to be more expensive than electric vehicles. The high cost of hydrogen production, storage, and transportation technologies contributes to this price disparity. However, as technological advancements and economies of scale kick in, the cost of hydrogen engine cars is expected to decrease. Electric vehicles, on the other hand, have seen a reduction in prices over the years, thanks to advancements in battery technology and increased manufacturing volume.
Government Support and Policies
Government support and policies play a crucial role in shaping the future of hydrogen and electric engine cars. Incentives, subsidies, and favorable regulations can accelerate the adoption of sustainable transportation technologies. Many countries and regions have already implemented measures to promote electric vehicle adoption, including financial incentives, tax credits, and the establishment of charging infrastructure. Similarly, governments can play a pivotal role in fostering the growth of hydrogen infrastructure and promoting research and development in the hydrogen sector.
Future Prospects
While it is difficult to predict with certainty which technology will dominate the automotive industry in the future, both hydrogen and electric engine cars are likely to coexist. The specific use cases, regional factors, and advancements in technology will determine their respective market shares. It is possible that hydrogen engine cars may find a niche in long-distance transportation or heavy-duty applications, while electric vehicles continue to gain traction in urban areas and short-distance commuting.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the race between hydrogen and electric engine cars is fueled by the collective goal of achieving sustainable transportation. Both technologies offer distinct advantages and face unique challenges. Hydrogen engine cars boast zero-emissions, fast refueling, and long driving range, but their limited infrastructure and higher costs hinder mass adoption. Electric engine cars, on the other hand, provide zero-emissions, energy efficiency, and lower operating costs, but face range limitations and charging infrastructure challenges. The future of transportation will likely involve a diverse mix of both technologies, driven by advancements in technology, government support, and public demand for greener and more sustainable options.![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
FAQs
Q1. Are hydrogen engine cars safe?
Hydrogen engine cars are designed with safety in mind. Stringent safety measures are in place to prevent hydrogen leakage and ensure safe handling and storage of the fuel. Additionally, hydrogen gas is lighter than air and quickly dissipates in case of a leak, minimizing the risk of explosions.
Q2. Can electric vehicles be charged at home?
Yes, electric vehicles can be charged at home using a standard electrical outlet or a dedicated home charging station. This convenience makes EV ownership more accessible and allows for overnight charging, ensuring a full battery in the morning.
Q3. How long do electric vehicle batteries last?
The lifespan of electric vehicle batteries varies depending on various factors, such as usage patterns, charging habits, and battery chemistry. Generally, modern electric vehicle batteries are designed to last several years, with most manufacturers offering warranties that cover battery performance for a certain mileage or time period.
Q4. Will hydrogen engine cars replace electric vehicles?
It is unlikely that hydrogen engine cars will completely replace electric vehicles. Both technologies have their own advantages and will likely coexist in the future, catering to different use cases and regional needs.
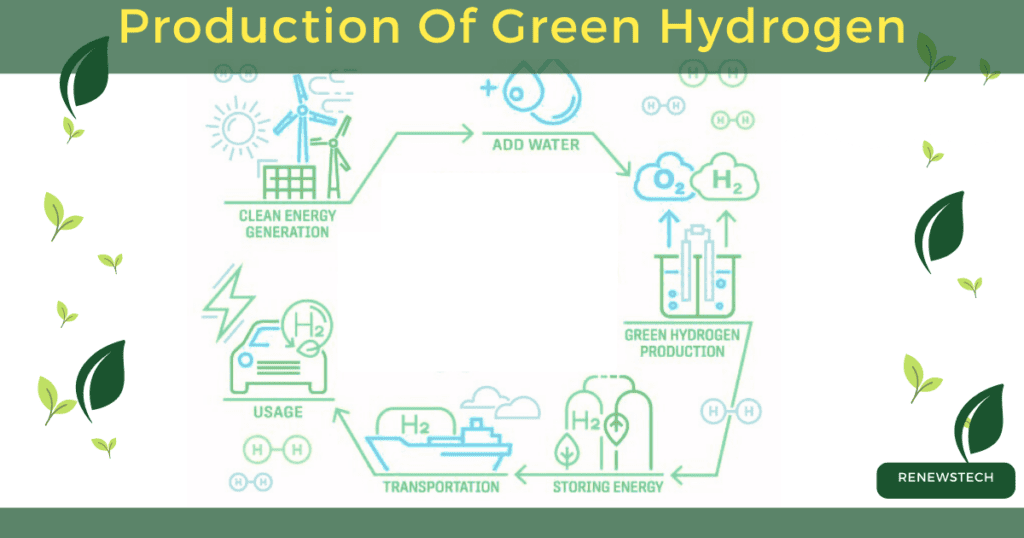
Q5. Can hydrogen be produced sustainably?
Yes, hydrogen can be produced sustainably by using renewable energy sources such as wind, solar, or hydroelectric power to generate electricity for the electrolysis process. This ensures that the production of hydrogen is carbon-neutral and aligns with the goal of achieving a sustainable energy future.