There are different types of Electric vehicles are categorised on several bases like battery size, power train configuration, charging time, driving range etc. Here we discuss, how EVs are classified on the bases of power train configuration. As we all known about the adoption of Electrical vehicle is rapidly improving, people are buying EVs rather than traditional vehicles. Before buying an EV we need to know what are different types of electric vehicle and which you must buy according to your need you can choose the type of your EV.
![]()
What is powertrain configuration:
The powertrain configuration consists of main components that works together to power and control the operation of EV
Battery
The battery is the primary source of energy for an EV. It stores energy that is used to power the electric motor and other components.
Electric Motor
The electric motor converts electrical energy stored in the battery into mechanical energy to propel the vehicle. It is a critical component of the EV’s powertrain configuration. One or more electric motors are used depends on the requirements. AC motors or DC motors are used.
Power Electronics
Power electronic converters, which converts the DC energy in to AC or DC to DC conversion depends on which type of motor is used. The power electronics converters manage the flow of energy between the battery and the electric motor. They control the voltage and current, and convert direct current (DC) power from the battery into alternating current (AC) power that is used by the electric motor.
Transmission
In an EV, the transmission controls the speed and torque of the electric motor. Some EVs do not have a traditional transmission, but instead use a single-speed transmission that is optimized for electric power.
Drivetrain
It is simply an energy transmission unit which transmits the mechanical energy from electric motor to the wheels, allowing it to move forward or backward.
The powertrain configuration of an EV is designed to be more efficient and environmentally friendly than traditional internal combustion engine vehicles. By eliminating the need for gasoline or diesel fuel, EVs have the potential to significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions and improve air quality. On the bases of powertrain configuration EVs are classified as follows
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Different Types of Electric Vehicle
1.Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs)
These are electric vehicles that are powered entirely by a battery and do not have an internal combustion engine. BEVs are designed to be recharged by plugging into an external power source, such as a charging station or a regular household outlet
2.Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs)
HEVs have both an electric motor and an internal combustion engine. The electric motor is powered by a battery that is charged by the internal combustion engine and regenerative braking.
Regenerative braking is a process that converts the kinetic energy of a moving vehicle into electrical energy, which can then be used to charge the vehicle’s battery. When the brakes are applied, the electric motor switches from a propulsion mode to a generator mode, and the kinetic energy of the vehicle is used to generate electricity that is sent back to the battery to store. HEVs cannot be charged by plugging into an external power source.
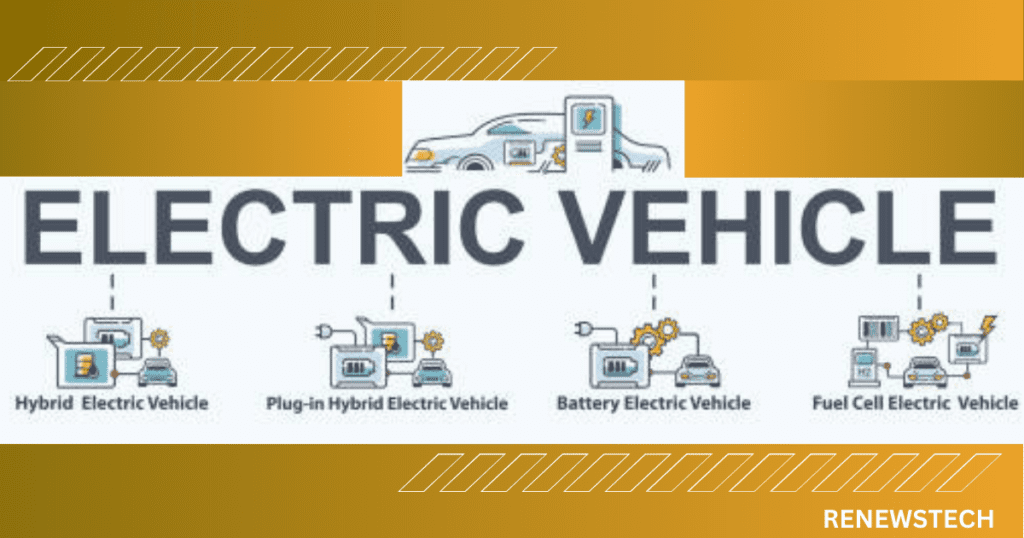

3.Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs)
PHEVs have both an electric motor and an internal combustion engine. They can be powered by either electricity or gasoline and can switch between the two power sources depending on the driving conditions. In PHEVs, regenerative braking is a crucial feature that helps to improve fuel efficiency and extend the vehicle’s driving range. PHEVs have a larger battery unit than HEVs and can be recharged by plugging into an external power source.
4.Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles (FCEVs)
FCEVs are powered by a fuel cell stack that generates electricity by combining hydrogen fuel with oxygen from the air, producing water and heat as byproducts. The electricity generated by the fuel cell stack is used to power the vehicle’s electric motor.
FCEVs are designed to be refuel with hydrogen gas, which is stored in high-pressure tanks onboard the vehicle. However, FCEVs also have a battery pack, which is used to store energy and provide additional power to the electric motor when needed. The battery pack can be charged externally using a charging port, similar to a battery electric vehicle (BEV).
The charging time for FCEV batteries is typically shorter than that of a BEV because the battery unit an FCEV is smaller, and its primary purpose is to provide additional power to the electric motor, rather than being the main source of power. However, the primary source of power for an FCEV is the fuel cell stack, which generates electricity continuously as long as hydrogen fuel is supplied to it. FCEVs can be charged externally using a charging port, but their primary source of power is the fuel cell stack, which generates electricity onboard the vehicle using hydrogen fuel and does not require external charging
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Comparison
| EV Type/Parameters | Battery Electric Vehicles | Hybrid Electric Vehicles | Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles | Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles |
| IC Engine | Absent | Present | Present | Absent |
| Electric Motor | Present | Present | Present | Present |
| External charging | Possible | Not possible | Possible | Possible |
| No. of power sources | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| Regenerative braking | Present | Present | Present | Present |
Conclusion
There is other several types of EV. Here in this article, we discussed working of an EV with powertrain configuration category, which includes different components working together to control the operation of EV. Each type of EV has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of which type to use depends on factors such as driving habits, charging infrastructure, and personal preferences.
FAQs
1.What is an all-electric powertrain configuration?
An all-electric powertrain configuration is where an electric motor is the only source of propulsion, and the vehicle is powered entirely by electricity from an onboard battery.
2.What is a hybrid powertrain configuration?
A hybrid powertrain configuration combines an electric motor and a gasoline engine to power the vehicle. The electric motor can provide additional power, particularly during acceleration, while the gasoline engine recharges the battery and powers the vehicle during extended driving periods.
3.Which powertrain configuration is the most environmentally friendly?
An all-electric powertrain configuration is generally considered the most environmentally friendly as it produces zero emissions and has the potential to use renewable energy sources.
4.Which powertrain configuration is the most cost-effective?
The cost-effectiveness of a powertrain configuration depends on a variety of factors, including purchase price, operating costs, and fuel efficiency. All-electric powertrain configurations tend to have lower operating costs and maintenance expenses, while plug-in hybrids may have a lower purchase price.
5.Can a powertrain configuration be changed after purchase?
No, the powertrain configuration of an electric vehicle cannot be changed after purchase as it is determined by the manufacturer and integrated into the vehicle’s design.