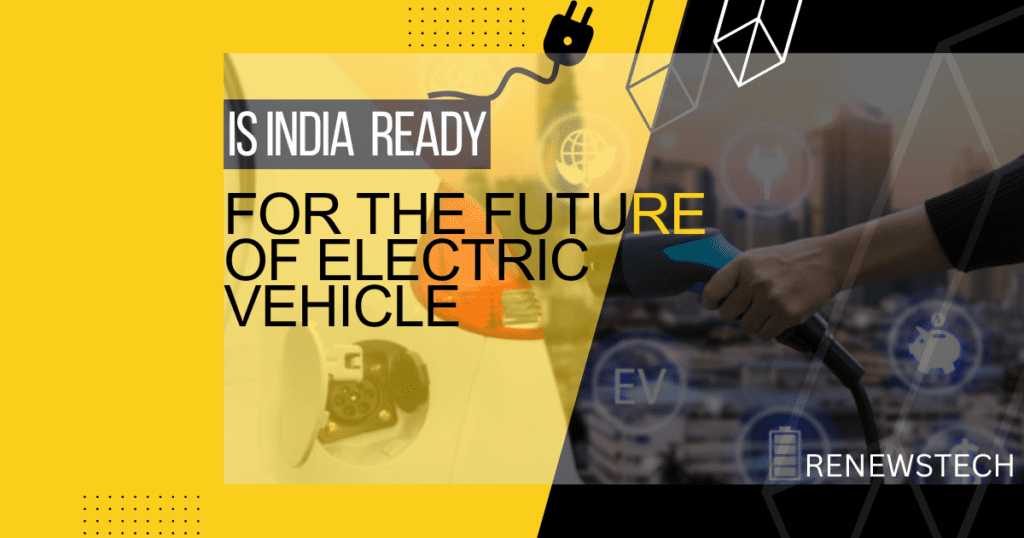
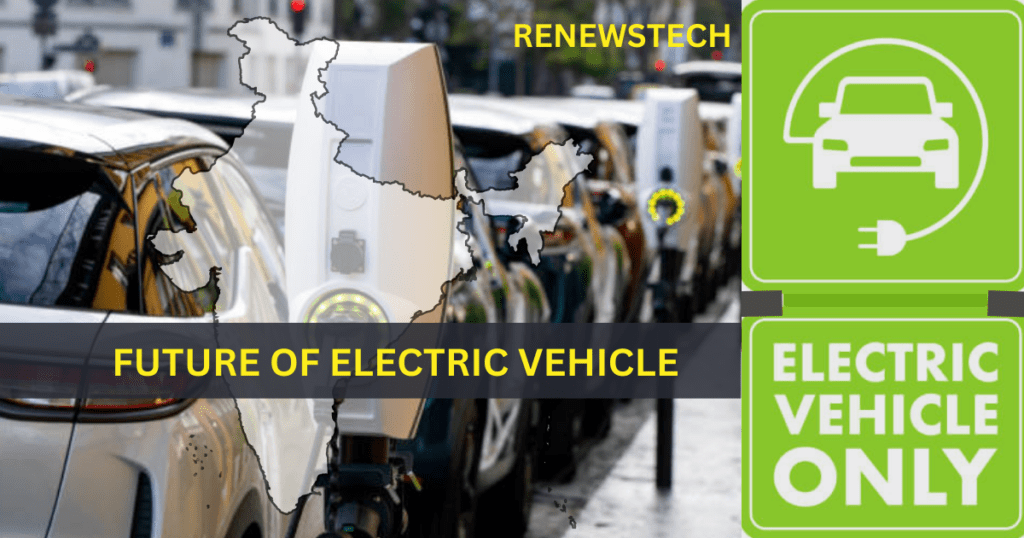
The future of Electric Vehicles in India looks promising, with the Indian government setting ambitious targets for the adoption of electric vehicles in the country. In 2018, the government launched the National Electric Mobility Mission Plan (NEMMP), which aims to achieve 30% electric vehicle penetration by 2030.To support the growth of EVs, the Indian government has implemented several initiatives, including tax incentives, subsidies, and investment in charging infrastructure. Additionally, major automobile manufacturers in India have started to focus on electric vehicle production, with many launching new EV models and investing in battery manufacturing plants. India, a developing country, is taking significant steps to shift towards sustainable development and reduce its carbon footprint. The transportation sector is one of the major contributors to India’s carbon emissions, and therefore, the country is exploring various alternatives to fossil fuel-based vehicles. One of the most promising alternatives is electric vehicles (EVs), which have the potential to significantly reduce the country’s carbon emissions and dependence on imported oil. However, there are several challenges that need to be addressed before India can fully embrace EVs. In this blog, we will discuss whether India is ready for EVs and the factors that need to be considered in this transition for the future of Electric Vehicle in India. Before talking about the future of electric vehicle first let’s talk about the need of adoption of EV and is India making action plan to fulfil these needs.
![]()
WHY INDIA NEEDS ADOPTION OF EV
Air pollution due to transportation:
This is a significant problem in India. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), 14 of the world’s 20 most polluted cities are in India, and transportation is a major contributor to this issue.
Not only in urban but also in rural areas, high levels of air pollution are primarily caused by emissions from cars, trucks, and other vehicles. The burning of fossil fuels in these vehicles releases harmful pollutants such as carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter into the air, which can cause respiratory problems and other health issues. In addition to this, the rapid increase in the number of vehicles on Indian roads has led to traffic congestion, further exacerbating air pollution levels. The lack of effective public transportation infrastructure, including inadequate or non-existent public transit systems, has resulted in more people relying on personal vehicles, leading to higher emissions.
The Indian government has taken some measures to address the issue of air pollution from transportation, such as the implementation of stricter emission norms for vehicles and the promotion of electric vehicles. However, more significant efforts are needed to improve public transportation infrastructure, promote active transportation such as cycling and walking, and reduce the number of vehicles on the roads. These measures can help mitigate air pollution and improve public health in India.
Climate change:
India has taken several steps to fight against climate change, including the adoption of renewable energy sources and the promotion of electric vehicles. The Indian government had set a target of achieving 175 GW of renewable energy capacity by 2022, which includes 100 GW of solar, 60 GW of wind, 10 GW of bioenergy, and 5 GW of small hydro power. This was expected to help reduce India’s greenhouse gas emissions and promote sustainable development. Regarding EVs, India has announced several initiatives to promote their adoption. In 2018, the government launched the FAME (Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Hybrid and Electric Vehicles) India scheme, which provides incentives for the adoption of EVs and supports the development of charging infrastructure. The government has also announced plans to achieve 100% electric mobility by 2030, although this target has been revised to a more realistic 30% by 2030 due to various challenges.
Dependency on Fossil Fuel:
India is highly dependent on fossil fuels to meet its energy needs. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), 90% of the India’s transportation fuel needs depends on oil and gas. India’s dependency on fossil fuels has several negative impacts, including air pollution, greenhouse gas emissions, and economic vulnerability to global oil price fluctuations. To reduce its dependency on fossil fuels, India has announced several initiatives to promote the adoption of electric vehicles (EVs), such as the FAME India scheme, which provides incentives for EV adoption and supports the development of charging infrastructure. EV adoption can reduce the demand for oil, thus reducing the country’s oil imports and improving its balance of trade.
To Ensure the Energy Security:
As the demand for electricity increases with the adoption of EVs, the use of domestically generated renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power can be expanded, reducing India’s dependence on imported oil and increasing energy security. Promoting the adoption of EVs can play a significant role in enhancing India’s energy security by reducing dependence on imported oil, diversifying the energy mix, and promoting domestic production of EVs and components. However, it will require sustained efforts from the government, private sector, and society to make it a reality.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
HOW INDIA IS MOVING FORWARD AND GETTING READY FOR THE FUTURE OF ELECTRIC VEHICLE
For looking towards the bright future of Electric vehicles in India, we need to have a look over the steps taken by government and private sectors in India.

Charging Infrastructure:
While there has been some progress in setting up charging infrastructure in India, the country still has a long way to go in terms of building a comprehensive charging network. As of March 2021, there were around 1,800 public charging stations across India, but this is still a small number compared to the size of the country and the number of EVs on the road. However, several public and private players have announced plans to set up charging infrastructure across the country, which could help accelerate EV adoption.
Battery Technology:
India is making progress in battery manufacturing, with several companies announcing plans to set up battery manufacturing plants in the country. However, the country still depends on imports for most of its battery needs. To reduce the cost of batteries and make EVs more affordable, local manufacturing needs to be scaled up, and more research and development efforts need to be focused on improving battery technology.
Government Support:
The Indian government has announced several initiatives to support the EV industry, including tax exemptions, incentives for manufacturers, and subsidies for buyers. However, the impact of these measures has been limited so far, and more significant policy changes and investments are needed to accelerate the adoption of EVs.
Awareness and Education:
Awareness and education about EVs have been slowly increasing in India, but more needs to be done to make people aware of the benefits of EVs and dispel misconceptions about them. Government-led campaigns, along with private sector initiatives, can help educate consumers about the benefits of EVs and increase their adoption.
Localization of EV Production:
Several international automakers have announced plans to localize the production of EVs and related components in India. This could help reduce the cost of EVs and make them more affordable for Indian consumers. However, local start-ups need to be encouraged to enter the EV market to promote competition and innovation.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
CONCLISION
India has taken significant steps towards the adoption of electric vehicles, but there is still a long way to go before EVs become the norm in the country. The Indian government needs to address several challenges, such as the high cost of EVs, lack of charging infrastructure, and limited awareness among consumers. Additionally, the Indian automobile industry needs to focus on developing and manufacturing EVs that meet the unique requirements of Indian roads and driving conditions. The shift towards electric vehicles is not only necessary for reducing India’s carbon footprint but also has the potential to create new job opportunities and improve the country’s energy security. Therefore, it is crucial for all stakeholders, including the industry, government and consumers to work together towards the future of Electric Vehicles in India.